14.13 Optimize Codons
The option Optimize Codons... from the Cloning menu allows you to adapt a nucleotide sequence to the genetic code and preferred codon usage of a particular expression host. The resulting sequence is optimized to avoid use of codons that rarely occur in the highly expressed genes of the expression host, thus increasing its expression level when cloned into that species. In addition, the resulting sequence can be forced to avoid cleavage sites for a set of restriction enzymes that you specify.
This tool calculates the Codon Adaptation Index (CAI) of a gene sequence as the geometric mean of the relative adaptiveness (w) of the codons in the sequence, as defined in Sharp and Li, 1987. Relative adaptiveness is calculated from Codon Usage Tables supplied by EMBOSS, which calculate the relative codon usage of a selected set of genes in the target organism. The optimized sequence returned is the one for which CAI is maximised.
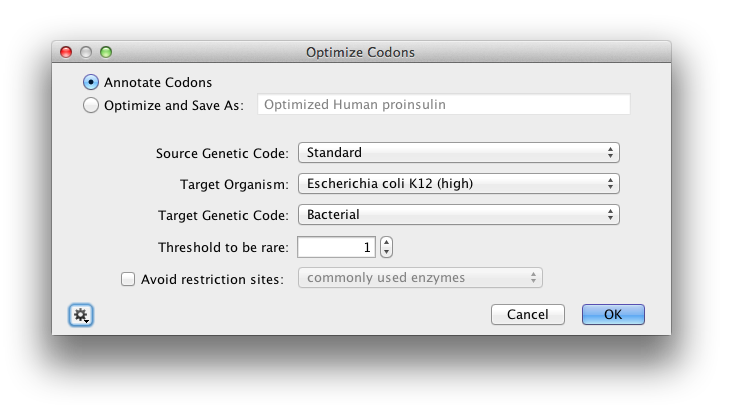
You can configure the following options (Figure 14.8
):
- Annotate Codons creates an annotation track on the existing sequence with an annotation on each codon that is changed in the target sequence. Each annotation has qualifiers that specify the original codon, the replacement codon, and the relative adaptiveness value (W) of the replacement codon calculated for the selected target organism codon utilization table.
- Optimize and Save As creates a new sequence document that contains the result codons and the same annotation track and annotations as described in the previous option. If multiple input sequences are selected the result sequences are placed in a single sequence list document. Enter the name of the new document in the text input box of this option.
- Source Genetic Code lets you select the genetic code to be used when translating the source sequences. If you have selected multiple source sequence documents with different genetic codes, the choice “Multiple Values” will be available to indicate that the genetic code associated with each document should be used. You can select a genetic code other that the one that is shown as the default for the selected input documents if you want to override the default.
- Target Organism lets you select a Codon Usage Table for the target expression host. Each table contains the codon usage statistics for a selected set of genes of the organism. In addition to the codon usage tables included with Geneious Prime, you can import custom codon usage tables in GCG CodonFrequency and EMBOSS cusp formats. For further instructions, see How do I create a custom codon usage table?.
- Target Genetic Code lets you specify the genetic code of the target organism. The EMBOSS CUT file format that is used for the Target Organism codon usage data does not contain a field for the genetic code. You must select the correct genetic code for the target organism that you select.
- Threshold to be rare lets you specify the relative adaptiveness value (W) for a codon below which the codon is considered to be “rare” and will be replaced with the highest value synonymous codon. Set the threshold to 1 to change all codons that are not the highest value in their synonymous set. Use threshold of 0 to only replace codons that code for the wrong amino acid in the target genetic code or that have to be changed to avoid restriction sites.
- Avoid restriction sites lets you select a set of enzymes that you intend to use to cut the target sequence. If you select an enzyme set with this option, the result sequence will not include any sites that match a recognition sequence in the set. The enzyme set choices are the same as are used in 14.1
.
After configuring your options, click OK to start the analysis and annotate the optimized codons on the sequence or create the new sequence document.